Recently, a news was circulated in a circle of friends.
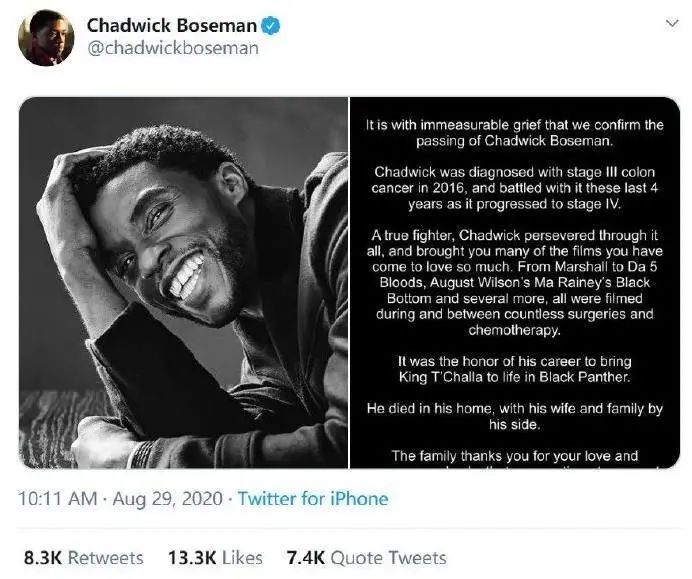
(Devik bosman’s social account announced the news of his death)
According to foreign media reports, on August 28th, local time, Chadwick Boseman, a famous actor and leading actor in Black Panther, died of colon cancer at the age of 43. It is reported that he was already in the third stage when he discovered intestinal cancer, and he could not be spared after fighting the disease for four years.
In fact, colorectal cancer has become the third most common malignant tumor in men and the second most common malignant tumor in women worldwide. In China, due to the improvement of living standards in recent years, the diet structure with high fat, high calorie, high protein and low dietary fiber, lack of exercise, bad living habits and other factors, the incidence of colorectal cancer has obviously accelerated and the onset age has advanced. The latest data from the National Cancer Registry show that the incidence of colorectal cancer among urban and rural residents in China is increasing year by year:
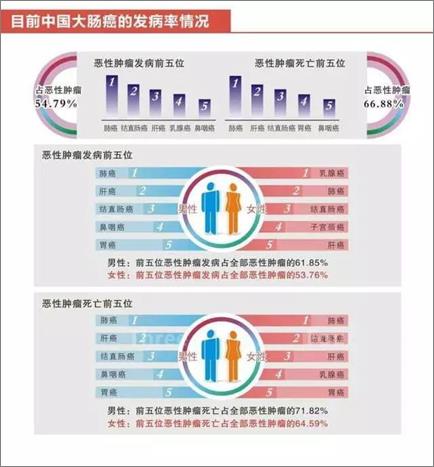
(Image from the Internet)
Colorectal cancer is a common malignant tumor of digestive tract, including colon cancer and rectal cancer. Early colorectal cancer is often asymptomatic, but with the development of cancer, symptoms gradually appear:
1. The regularity of defecation has changed. The frequency of defecation is increased or particularly difficult, diarrhea, constipation or alternating diarrhea and constipation, and sometimes it is urgent and then heavy.
2. Abnormal stool shape. The stool is thin, flat or angular.
3. The nature of stool changes. There is blood or mucus in the stool, and the stool is not formed.
4. Symptoms of digestive tract. Abdominal pain, bloating, indigestion, loss of appetite, etc.
5. There is a mass in the abdomen and there is fixed pain.
6. Systemic cachexia symptoms such as emaciation and anemia …

At this time, it has often progressed to the middle and late stages, missed the best treatment opportunity, and it is too late to regret it! Even if the life is saved through surgery or various treatment methods, the quality of life is relatively poor.
Therefore, early diagnosis has become a key link in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer! In fact, for the terrible colorectal cancer, if it is found in the early stage, the survival rate of patients is very high, and some even reach more than 90%.
The Lancet once published a study saying that a screening for intestinal cancer can reduce the risk of intestinal cancer by more than one third and save countless lives. According to the data of CDC, raising the screening rate of colorectal cancer to 60%~80% can reduce the incidence of colorectal cancer by 22% (277,000 people) and the death of colorectal cancer by 33% (203,000 people).
More than 85% of colorectal cancer comes from untreated adenomatous polyp, which is a long process, and the process is roughly as follows:
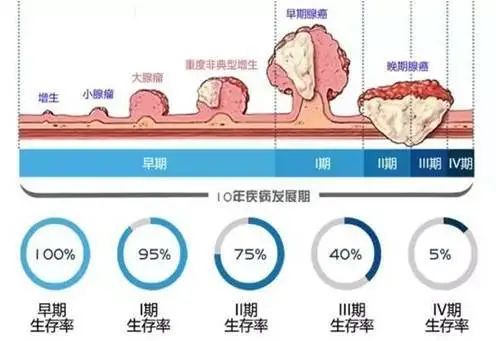
(Image from the Internet)
It can be seen that the canceration process of some colorectal cancers lasts for 10-15 years. As long as we can do a good job in screening and surgical resection at the benign stage, some cases can be completely cured without radiotherapy and chemotherapy. If we can maintain a healthy lifestyle and not give the disease an opportunity, some polyps will never have a chance to form, so as to achieve real scientific prevention!
So, what methods can be used to screen for colorectal cancer? Let’s take a look at the advantages and disadvantages of various screening methods:
1. Fecal occult blood test (FOBT)
Monoclonal immune reagent is used to detect whether there is trace bleeding in stool, and then indirectly judge whether there is hemorrhagic disease in intestine. According to statistics, 50%~60% patients with colorectal cancer and 30% patients with colorectal polyps are all positive for FOBT test. If the result is positive, further colonoscopy is needed. FOBT is also the only screening method that has been proved to effectively reduce the mortality of colorectal cancer, which can reduce the mortality of colorectal cancer by 18%.
Advantages: The method is simple and feasible, and can be used as a screening method for general survey.
Disadvantages: the false positive rate is high, hemorrhoids, anal fissure, perianal eczema, physiological period and other factors can lead to positive results, lacking screening specificity.
2. Digital rectal examination
Anal digital examination is mainly aimed at the rectal part, and it is based on the doctor’s experience and feel to judge whether there is a tumor in the patient’s rectum. The length of the doctor’s finger can touch the middle and lower rectum, so the accuracy of this examination is about 80%. Relevant data show that the lower rectal cancer is far more common in China than abroad, accounting for 77.5% of rectal cancer, so most rectal cancer can be touched during digital rectal examination.
Advantages: good quality and low price, high cost performance, and can be used as a means of general survey and screening.
Disadvantages: the "chrysanthemum" is tight and the discomfort is obvious. Initially judge whether there are lesions in rectum and surrounding organs 7~10cm away from anus; But it has no significance for high colon lesions. It is closely related to the experience of examining doctors, and the overall accuracy is not so high.
Anyone who has blood in the stool or changes in stool habits and has no abnormality by rectal digital examination should be examined by colonoscopy.
3. colonoscopy
Include colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, proctoscopy, etc. Colonoscopy is the process of observing colonic lesions (such as inflammation, polyps, tumors, etc.) from the anus, through the rectum and sigmoid colon, and to the ileocecal part by using electronic colonoscopy. At present, most hospitals adopt fiber colonoscopy, which is suitable for detecting unexplained changes in stool habits, bloody stool, abdominal pain, indigestion and so on. Colonoscopy is one of the safe and effective methods to diagnose colorectal diseases, which can clearly find intestinal lesions through direct examination of the intestine.
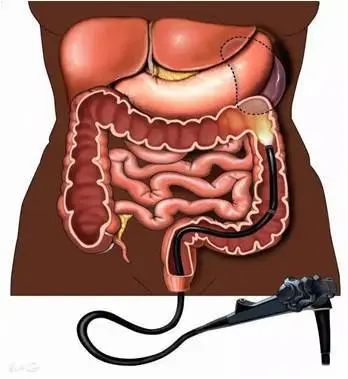
According to medical statistics, it is found that 60~70% of intestinal cancer in China occurs in rectum and sigmoid colon. Therefore, rectal endoscopy and sigmoidoscopy can directly find tumors below the middle section of anal canal, rectum and sigmoid colon.
Advantages: colonoscopy is the first choice for the prevention and diagnosis of colorectal cancer, and the best means is intuitive and clear. Some gastrointestinal polyps and early cancer can be cured by minimally invasive treatment under endoscope.
Disadvantages: colonoscopy cannot be used as a large-scale screening method. The inspection cost is higher than the first two inspections; Colonoscopy requires specialized doctors to undergo professional training and long-term practice. The poor degree, the trouble degree of bowel cleaning preparation and the pain degree of inspection process make many people flinch.
Therefore, before colonoscopy, some pre-examination items can be done to screen out the suspicious population of colorectal cancer, improve the positive rate of colonoscopy, and make the subjects worthwhile. However, we can’t refuse colonoscopy because we are afraid of being "exploded". Patients who meet the anesthesia indications can choose painless colonoscopy.
4. Blood tumor index examination
Among tumor markers, such as CEA, CA199, CA242 and CA724 play an important role in the detection of colorectal cancer. In the latest guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer, it is also mentioned that these indicators can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and curative effect judgment of colorectal cancer.
Advantages: simple and easy, blood test.
Disadvantages: The single index of traditional tumor markers can not meet the screening requirements in detection sensitivity and specificity, and there are many influencing factors.
Therefore, multi-index combined detection is one of the principles of tumor markers. Studies have shown that the combined use of CEA, CA199 and fecal occult blood can improve the sensitivity of colorectal cancer to 83.1%, which is much higher than that of single index detection.
5. Tumor gene detection and fecal DNA detection.
Gene detection is a frontier technology for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. By detecting the methylation level of some specific genes in blood or feces free DNA, colorectal cancer screening can be carried out.
Advantages: simple and easy to operate, with higher sensitivity and specificity.
Disadvantages: the detection cost is high, and it is difficult to be used for large-scale population screening of colorectal cancer.
6. Imaging examination, gastrointestinal CT virtual endoscopy
CT virtual colonoscopy (CTC), also called virtual colonoscopy and virtual scene, is a safe and non-invasive colon examination method. Three-dimensional CT examination of the large intestine (CTC) is an ideal alternative when the screening object is unable or unwilling to undergo colonoscopy screening. In short, it is a technique to scan the whole colon in supine position and prone position with multi-slice spiral CT, and then edit and reconstruct the data obtained by photography after image processing, so as to generate three-dimensional images of the intestine and check the potential lesions.
Advantages: the risk of colon perforation is low, the requirement of bowel cleaning is not high, there is no obvious contraindication, the examination time is short, convenient and painless, and the X-ray radiation is lower than that of barium enema examination. For polyps larger than 1 cm, the detection sensitivity is high. At the same time, some extraintestinal lesions can be found.
Disadvantages: CTC is a virtual image, which can not show the true color of intestinal mucosa, nor can it observe the subtle changes of blood vessels and mucosa. The ability to identify shallow concave, slight protuberance and flat lesions is poor; Lesions less than 5mm, or flat lesions with little uplift or with the difference of mucosal color as an important clue can not be judged. It is only an indirect observation of the lesion, and samples cannot be taken for pathological diagnosis or treatment; There is radiation damage; The cost is higher. At present, this method has not been popularized in China.
Its limitations are obvious, and it can’t completely replace the traditional colonoscopy. However, for those friends who really don’t want to do colonoscopy, combining fecal occult blood test (chemical method and immune method) and fecal DNA test can also be used as a temporary means for early cancer screening. However, in order to find early cancer and precancerous lesions, such as adenomatous polyp, flat polyp, etc., traditional colonoscopy is more reliable.
in conclusion
"Chrysanthemum" is no small matter, so don’t be nervous when checking it.
To keep the intestines safe, screening is indispensable!
Authors: Surgery, East China Sanatorium
Attending physician in Zhou Lu
All names and places are pseudonyms, and if there are similarities, it is purely coincidental.